Rationale
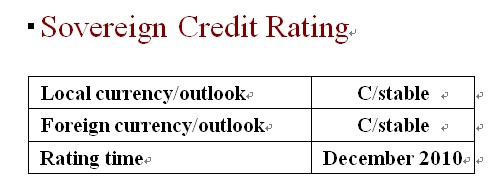
Dagong assigns “C” to the local currency and foreign
currency credit ratings for the Republic of Sudan (hereinafter referred to as “Sudan”)
based on comprehensive consideration of such factors as its volatile political
situation, low level of economic and financial development, highly indebted
government and weak foreign exchange reserves.
The Sudanese government has not released its debt report,
so the public is unable to learn its debt scale accurately. According to the
IMF's estimate, the central government’s debt-to-GDP ratio has already surpassed
80%; moreover, the public debt-to-GDP ratio is as high as 105.1%. Both of the
ratios belong to the highest level in developing countries, which indicates the
heavy debt burden of the Sudanese Government. In fact, most of the government
debt is in arrears. In addition, the government planned a vast investment in the
domestic infrastructure, but limited by its fiscal strength, it has to rely
heavily on financing. However, the government’s financing requirement has been
restrained by the requests from its main creditors such as IMF and World Bank,
who demand the government to control its expenses and reduce non-concessional
loans. It is estimated that in the near future, the frail fiscal status of the
Sudanese government will not be improved effectively; and there will still be
the problems of insufficiency of developing expenditure and arrear of
debt.
On the whole, the Sudanese government has a weak capacity
for foreign and local currency debt repayment. The main reasons are as
follows:
l
North-South issue and the Darfur issue are unlikely to be completely resolved in the
near future, so the future tense situation will continue. The political
situation in Sudan will remain a long term
constraint to the development of economy and the government credit;
l
Sudan has a weak
economic basis and single economic structure and belongs to the most undeveloped
countries. Due to the impact of severe domestic and international political
situation, its abundant agricultural and oil resources have not been effectively
transformed into the driving force to promote economic
development;
l
Sudan’s financial
sector is small and undeveloped; its banking system is weak. High rate of
non-performing loans increases the government’s contingent liabilities, which
limits the government’s credit;
l
Sudan relies heavily on oil export revenues for its
fiscal revenue, and consequently, the stability of fiscal revenue is subject to
the fluctuation of international oil price to a great extent; its narrow tax
base and lower tax revenue limit the government’s ability to use tax policy to
regulate the economy;
l
Sudan’s foreign
exchange revenue relies heavily on oil exports as well as foreign direct
investment, so the international balance of payment is rather fragile, which
yields very weak foreign exchange reserves. While the external debt burden is
extremely heavy, there is an urgent need for debt relief from its main
creditors.
Outlook Both
the conflict between the central government and Southern government and the
conflict between the central government and Darfur armed groups cannot be fully
reconciled in a short term, but none of the single party can dominate the
domestic political situation just by itself with its current strength, which
determines that the political situation in Sudan will
continue to maintain the existing situation, and still be the key factor to
constrain the economic development, improvement of fiscal status and debt
service. Affected by this, the process of improving the environment of economic
development in Sudan and debt relief sought by the
government will be very slow. And the fragile balance of international payment
will continue. Therefore, Dagong keeps the stable outlook for
Sudan’s sovereign credit rating of
both the local currency and foreign currency in the next 1-2 years.
|